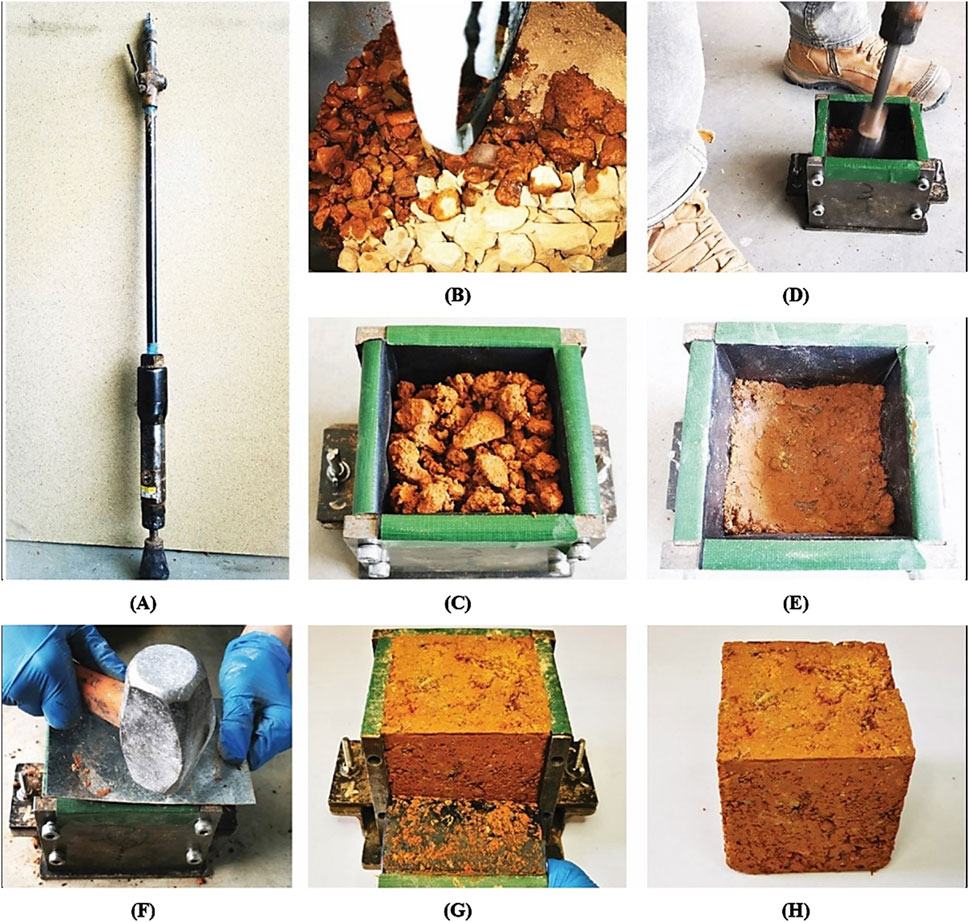
Rammed earth construction has gained increasing interest in recent years owing to sustainability demands in the construction industry and the advancement of digital fabrication techniques. However, the domination of cement-stabilized material in this industry poses environmental concerns, In this study, bio-based aternatives to cement are investigated through evaluating xanthan gum and animal glue as bio-binders. Results show that animal glue stabilized specimens demonstrate a 294% strength improvement over unstabilized rammed earth, while xanthan gum stabilized specimens achieve a 221% improvement.

Xanthan gum demonstrates suitability for dry mixing, and AG for wet mixing. Also, animal glue stabilized samples attain adequate reusability in terms of anti-fungal properties and fine particle distribution after crushing, which are less prominent in the xanthan gum stabilized samples.

The findings from this research demonstrate that these bio-binders have the potential to be viable alternatives to mainstream rammed earth construction methods, paving the way for advancing environmentally friendly rammed earth construction.
You can read the original article at www.frontiersin.org