Solar chimneys harness the power of the sun to generate electricity and provide natural ventilation and are proving to be an effective way to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions.
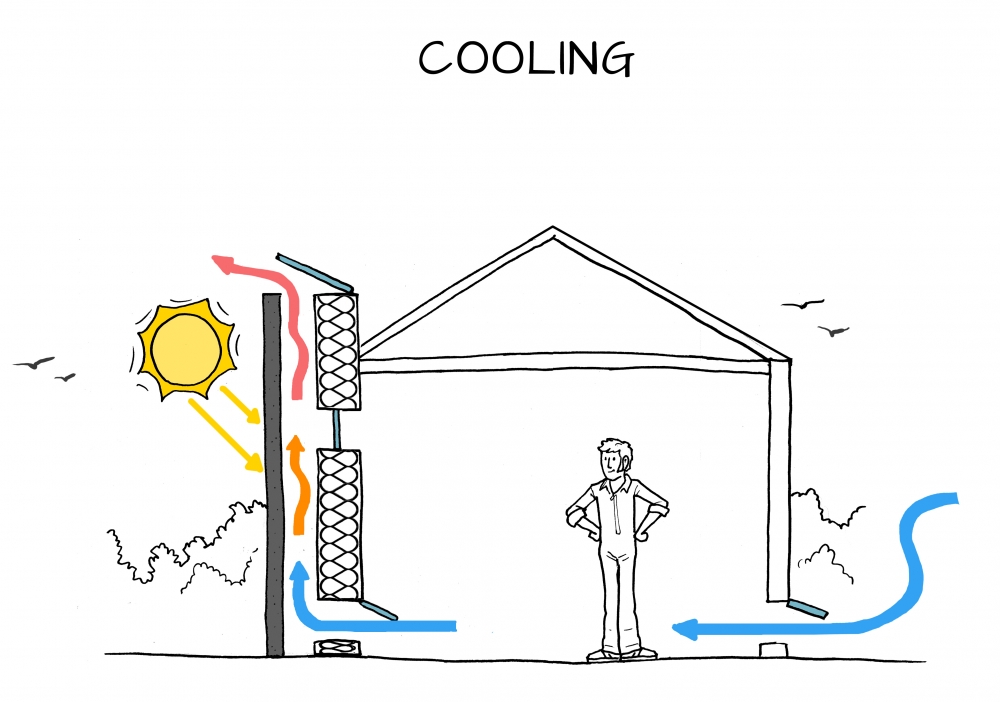 The basic principle behind solar chimneys is the greenhouse effect, where solar radiation is trapped and converted into heat and this heat is used to create an updraft, or a flow of air that rises through the chimney. As the warm air rises, it creates a vacuum at the base of the chimney, which draws in cooler air from the surrounding environment. This natural ventilation process helps to regulate the temperature inside the building and reduces the need for air conditioning and heating systems. By incorporating a turbine at the base of the chimney, the updraft created by the heated air can also be harnessed to generate power.
The basic principle behind solar chimneys is the greenhouse effect, where solar radiation is trapped and converted into heat and this heat is used to create an updraft, or a flow of air that rises through the chimney. As the warm air rises, it creates a vacuum at the base of the chimney, which draws in cooler air from the surrounding environment. This natural ventilation process helps to regulate the temperature inside the building and reduces the need for air conditioning and heating systems. By incorporating a turbine at the base of the chimney, the updraft created by the heated air can also be harnessed to generate power.
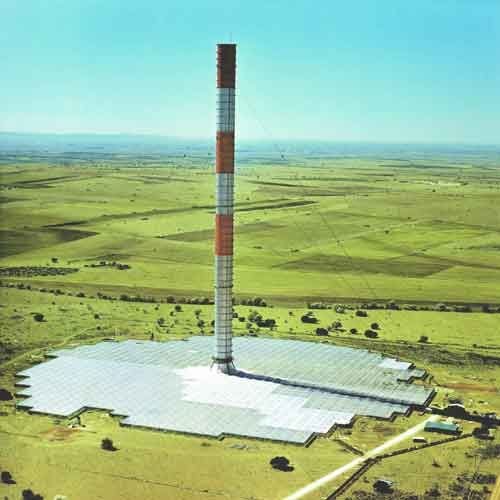 One of the most notable examples of a solar chimney in action is the Manzanares Solar Chimney in Spain, which was built in the 1980s as a prototype for large-scale solar power generation. The 195-meter-tall tower was equipped with a turbine that generated electricity from the updraft created by the heated air.
One of the most notable examples of a solar chimney in action is the Manzanares Solar Chimney in Spain, which was built in the 1980s as a prototype for large-scale solar power generation. The 195-meter-tall tower was equipped with a turbine that generated electricity from the updraft created by the heated air.
 Solar chimneys are also being integrated into residential building designs as a way to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy costs. Homeowners can take advantage of natural ventilation and passive solar heating, reducing their reliance on air conditioning and heating systems.
Solar chimneys are also being integrated into residential building designs as a way to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy costs. Homeowners can take advantage of natural ventilation and passive solar heating, reducing their reliance on air conditioning and heating systems.
By harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity and provide natural ventilation, these structures have the potential to significantly reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. As architects and engineers continue to explore new ways to incorporate solar chimneys into modern building designs, it is clear that this ancient concept has a bright future in meeting our modern energy needs.
You can read the original article at www.energyportal.eu

